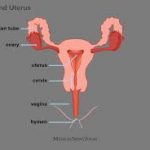
Gynecological cancer refers to the cancers that begin in the female reproductive system. Vaginal cancer falls under the ‘Gynaecological cancer’ category. Vaginal cancer is the overgrowth of vagina cells. The vagina is a muscular canal that starts at the cervix and opens at the vulva. The vaginal walls have multiple folds. It helps the vagina to expand during sex or the child-birth.
What are the signs & symptoms?
The common symptoms of vaginal cancer are vaginal discharge, constipation, a lump in the vagina, pelvic pain, painful and frequent urination.
What are the diagnostic tests for vaginal cancer?
Vaginal biopsy: The doctor removes the pieces of the cancerous part of the vagina with a long, hollow needle. It is the only way to assure if you have cancer.
Colposcopy: The doctor takes a detailed look at the inside of the vagina with a lighted magnifying device. The device stays outside the body.
CT scan creates detailed images of the body using x-rays. A CT scan detects the spread of cancer outside the vagina.
MRI scan uses radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed images. MRI helps to detect cancer spread.
PET scan detects the cancer spread. The doctor puts a small amount of a low-level radioactive substance into the blood. The substance attaches to the cancer cells. A special camera shows any areas of radioactivity.
How advanced is my vaginal cancer?
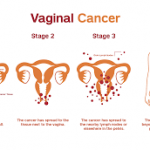
The doctor identifies the spread of vaginal cancer or the stage of cancer and decides the types of treatment required. These are based on the cancer growth or cancer spread.
Vaginal cancer can be classified as stages 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. Stage 0 is carcinoma in situ. The lower number indicates minimum cancer spread. A higher number indicates cancer growth or spread outside the vagina.
You can talk with your doctor about the stages.
What are the suitable treatments for me?
Several kinds of treatment are available for ovarian cancer, including surgery, radiation, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy.
SURGERY
Surgery helps to cure or control cancer and make symptoms better. It helps to cure vaginal cancer if not spread to other body parts. The traditional vaginal cancer surgeries are wide local excision, vaginectomy, lymph node dissection, pelvic exenteration, and total hysterectomy.
The common side effects of cancer surgery are pain, nausea, infection, scarring, loss of sensation, and changed bowel habits.
Ask the doctor about the kind of surgery needed and what to expect.
RADIATION THERAPY
Radiation destroys cancer cells left in the vagina after surgery. There are two ways to treat vaginal cancer with radiation. The first is by aiming the rays at the vagina from a machine outside the body. The second is by putting radioactive pellets, or tiny seeds, into the vagina near the ovaries.
The common side effects are fatigue (tiredness), diarrhea (dysentery), vaginal pain, dryness, and skin change.
Most side effects may improve after radiation ends. Ask your doctor about what to expect.
CHEMOTHERAPY
It is an uncommon treatment for vaginal cancer. You can take chemo medicines intravenously or orally. Topical chemotherapy is helpful for squamous cell vaginal cancer. The drugs spread through the body via the blood. Chemo is divided into cycles or rounds. After every cycle of treatment, there is rest time. Chemo is helpful if cancer has spread outside the vagina.
The common side effects are fatigue, body pain, infection, numbness, and hair loss. These side effects go away after chemo treatment ends. If you have side effects, discuss them with your doctor.
TARGETED THERAPY
It is helpful for certain types of vaginal cancer. These drugs majorly affect cancer cells and rarely normal cells. The drugs move inside the cancer cells and block particular proteins or enzymes that nourish cancer cells.
Delayed wound healing, bleeding, high blood pressure, and kidney ailments are the common side effects. Ask your doctor if any complications arise.
What are the other treatment options?
The other treatment options may or may not be standard medical treatments. These treatments include vitamins, herbs, and diets. Talk to your doctor about other treatment options.
What to expect after treatment?
You may have fear of cancer recurrence. Visit your doctor every three months after the treatment ends. Do not skip follow-up visits. Your doctors will ask you about new symptoms. A physical examination and diagnostic tests may help to check recurrence.
For the first year, the follow-up visits may be every three months. After the first year, follow-up visits might be every six months, and then at once a year after five years.
Dealing with cancer is challenging. Ankr can help you find the best treatment and cut side effects by half! Sign up for free 30-day trial now (https://my.ankr.us/patientSignup) Ankr is the useful Cancer Platform in and around the USA. It offers the best modern treatment for cancer. Hence, improving the quality and life expectancy of the cancer patients.
