Table of Contents
What is headache?
Headache is pain that occurs in your head, upper neck, or even your face. There are several different types of headaches. Migraines and tension headaches are the most common. Other types are cluster headaches and rebound headaches.
A migraine is an intense, pounding headache. You can get them once or often, and they can last for hours or days. Migraines are more common in women than men.
Migraines
Tension headaches
Tension headaches often are brought on by stress. They frequently start in the middle of the day. They may be mild or severe and get worse over time.
Sinus headaches
Sinus headaches are caused by sinus pressure. Your sinuses are small, air-filled spaces located behind your nose, cheekbones, and forehead. When your sinuses get irritated by an infection or allergies, these spaces can swell (become inflamed). This irritation also triggers your sinuses to begin overproducing mucus. Both of these contribute to sinus pressure.
Rebound headaches
People who have problems with medicine or substance abuse get rebound headaches. These headaches occur most days early in the morning. They also are sometimes referred to as medication-overuse headaches.
How bad is my headache?
Your clinic team will use this scale (see figure on right) to measure how bad your pain is.
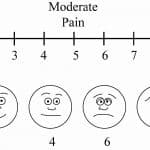
Mild: Pain score of 3 or less on the VAS scale. This pain should not stop you from doing activities of daily life (like grocery shopping, laundry, cooking). Most of the time, mild headaches can be safely managed at home by following the tips given in the section below.
Moderate: Pain score of 4 to 6. This pain stops you from doing instrumental activities of daily life (preparing meals, managing money, shopping, doing housework, and using a telephone).
Severe: Pain score of 7 or higher. This pain is bad enough to stop you from even the most basic (self-care) activities of daily life like eating, dressing, getting into or out of a bed or chair, taking a bath or shower, and using the toilet.
How to manage mild headache?
Keep track of headache using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the discomfort to your doctor or nurse.
You may be able to lower how many headaches you have by identifying what causes your headaches.
Migraines
Medicine to prevent migraines may be helpful if your headaches happen more than 2 times a month. Preventive medications for migraines can include prescription drugs often used to treat other ailments. Anti-seizure medicines, antidepressants, medicines to lower blood pressure, and even Botox injections are some of the preventive medications your doctor may prescribe. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) inhibitors can also help prevent migraines.
There are also a number of non-medical treatments to help minimize migraine pain and frequency. One is an electrical stimulation device. It is a headband that you wear once a day for 20 minutes to stimulate the nerve linked to migraines. Another non-medical treatment is counseling aimed at helping you feel in more control of your migraines.
Tension headaches
Improved posture can help prevent your muscles from becoming tense or tight. You can practice this while you’re sitting and while you’re standing. While sitting, make sure your shoulders are back and your head isn’t slumped forward or backward. This is especially important as you work at your computer and look at your smartphone. When standing, make sure to hold your shoulders back while also tightening your stomach muscles. Straighten your neck and hold your head level.
Sinus headaches
Keeping sinuses moist and clean may help prevent sinus headaches. Consider adding a humidifier to your bedroom. This can help your nose from becoming dry and irritated. Talk to your doctor about also using a tool to flush out sinuses. Your doctor may recommend using a neti pot or bulb syringe. This will moisten sinuses and help clean out mucus, too.
Rebound headaches
Limit the use of pain relievers. Use them only when you need them and no more than twice a week. If you feel like you need to use them more often, talk to your doctor. Avoid caffeine when taking pain relievers. This is because many pain relievers already contain caffeine. A double dose of caffeine can cause a headache or make it worse.
How to manage moderate and severe headache?
Seek immediate medical attention if you’re experiencing the worst headache, lose vision or consciousness, uncontrollable vomiting, or if the headache lasts more than 72 hours with less than 4 hours pain-free.
What causes headache?
The exact cause of headaches varies and is not always known.
Cause of migraine:
- Change in body chemicals.
- Genetics.
- Environmental factors.
A lot of factors can cause tension headaches. These include:
- Stress.
- Sleep problems.
- Sinus and allergy problems.
- Stiff or sore muscles due jaw clenching or poor posture.
- Depression.
- Anxiety.
- Hormonal changes in women.
- Certain medicines.
- Certain foods and beverages.
Overuse of medicine is the main cause of rebound headaches. Be careful taking high doses of certain medicines. These include:
- pain medicines
- over-the-counter medicines
- sedatives
- tranquilizers
- ergotamine medicines
- other prescriptions
