The parotid gland cancer is a cancer of salivary glands. Various salivary glands are present near and inside the mouth. Therefore, many cancerous (malignant) and non-cancerous (benign) tumors can develop in the salivary glands.
Apart from the parotid gland, cancer may spread to other surrounding structures. Therefore, the prognosis depends on the type of salivary gland cancer and the stage of the disease.
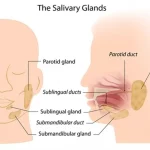
A Parotid gland is located in front of the ears. Approximately seven out of 10 salivary gland tumors develop in the parotid gland. In addition, most malignant (cancerous) tumors start at the parotid glands.
Types of parotid gland cancer
1. Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
The most common salivary gland cancer type begins in the parotid glands.
2. Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
It is slow-growing and is low-grade but difficult to eliminate since it spreads along nerves. The chances of recurrence are high following treatment (radiation and surgery).
3. Adenocarcinomas
It begins in gland cells (that secrete some substance).
Signs and symptoms of parotid gland cancer
- Weakness in the face, neck, jaw, or mouth
- Pain and numbness in the face, neck, jaw, or mouth
- Difficulty opening your mouth or moving your facial muscles
- Dysphagia (Painful swallowing)
- Bleeding from the mouth
Diagnostic tests
- CT scans provide images of masses within salivary glands using X-rays.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans create pictures of internal body structures using magnets and radio waves.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scans help identify cancerous masses using radioactive materials.
- A fine-needle biopsy removes a small tissue and fluid sample from a salivary gland tumor for further examination.
How to determine the severity of parotid cancer?
- Stage I: Tumors are tiny (not more than two centimeters across) and don’t spread to other body parts.
- Stage II: Tumors are between two and four centimeters. It remains in the original gland.
- Stage III: Tumors spread to the neck lymph nodes on the same side.
- Stage IV: Tumors spreads to lymph nodes and other body parts.
Physicians also give salivary gland tumors a specific grade of one to three to measure the growth rate of cancer cells.
- Grade 1: It is low-grade curable cancer. It doesn’t look different than your normal cells.
- Grade 2: It is moderate-grade cancer.
- Grade 3: It is high-grade cancer that proliferates.
What are the suitable treatment options?
Surgery
It is the primary treatment option for benign salivary gland tumors. It is helpful for slower-growing and early-stage cases. The surgery involves removing the part of the parotid gland or the entire parotid gland. In addition, the surgeon may remove lymph nodes and perform reconstructive work on the neck and face.
For malignant salivary gland cancers, doctors perform surgery like total parotidectomy to remove the tumor.
After surgery, recovery focuses on preventing infection and managing pain with the help of antibiotics and pain medications.
Radiation
It is not the first-line treatment for parotid cancer. But sometimes, it is an initial treatment when surgery isn’t an option. Surgery is followed by radiation therapy to the area affected by cancer and the draining lymph nodes. Radiation helps kill all cancer cells to minimize the chances of recurrence.
Chemotherapy
It isn’t the first-line treatment for parotid cancer, except in cases more advanced. However, you may have chemotherapy following surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. In addition, the doctors may recommend chemotherapy if cancer has spread from the salivary glands to other tissues outside the head and neck.
Alternative treatment options
The viable alternative options may or may not be standard treatment. It includes vitamins, herbs, and diet. Some of these may be useful. A few may be harmful. Discuss with the doctor other suitable treatment.
What to expect after treatment?
Regular post-treatment follow-up is recommended to detect early recurrences and to monitor for complications. Do not skip follow-up visits. Your doctors will ask you about new symptoms. A physical examination and diagnostic tests may help to check recurrence. For the first year, the follow-up visits may be every three months. After the first year, follow-up visits might be every six months and then once a year after five years.
Dealing with cancer is challenging and Ankr can help you. Ankr is a popular Cancer Platform in and around the USA. It offers the best modern treatment for cancer. Hence, improving the quality and life expectancy of cancer patients. Visit us at https://ankr.us
