Table of Contents
What is dysphagia?
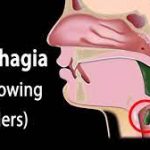
Dysphagia or painful swallowing is difficulty in passing food or liquid down the throat. It can be painful. In some cases, swallowing is impossible. Some people may gag, cough, or choke while swallowing. Others may feel like food is stuck in their throat. Dysphagia can occur at any age. It’s more common in older adults.
How bad is my dysphagia?
Mild: It may take longer to pass food through the esophagus. Other symptoms are persistent drooling of saliva and gurgly sound while eating or drinking.
Moderate: You may experience coughing, choking and pain on swallowing. Other symptoms are being unable to chew food properly and heartburn.
Severe: Solids and liquids do not pass at all down the esophagus. Visit your doctor if eating a meal takes more than 30 minutes. Other symptoms are nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath while eating and drinking, frequent chest infections without any reason.
How to manage mild dysphagia?
Keep track of your pain while swallowing using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the discomfort to your doctor or nurse.
- Eat soft, smooth, mash or blend foods (yogurt or pudding).
- Use a straw to drink liquids and soft foods.
- Eat cold or room-temperature foods to reduce pain.
- Take small bites. Chew slowly and thoroughly.
- Eat small, frequent meals.
- Sit upright when eating or drinking.
- Avoid dry, coarse, or hard foods.
- Drink meal replacement or nutritional supplement beverages.
How to manage moderate and severe dysphagia?
- Trouble swallowing accompanied by weight loss, regurgitation or vomiting
- A sensation that food is stuck in your throat or chest
- Persistent drooling (which indicates you’re having trouble swallowing saliva)
- Inability to chew food properly
- A wet, gurgling voice while eating or drinking
- Coughing while eating or drinking
- Difficulty breathing (rapid or shallow breathing, shortness of breath or wheezing)
- Chest pain
- Chills
- Fever
What causes dysphagia (painful swallowing)?
- Radiation therapy
- Surgery
- Chemotherapy
Some side effects of cancer treatment may cause swallowing difficulties:
- Fibrosis (scarring or stiffness in the throat, esophagus, or mouth).
- Infections of the mouth or esophagus.
- Swelling or narrowing of the throat or esophagus.
- Physical changes to the mouth, jaws, throat, or esophagus after surgery.
- Mucositis (soreness, pain, or inflammation in the throat, esophagus, or mouth).
- Xerostomia or dry mouth.
