Uterine cancer falls under the ‘Gynaecological cancer’ category. It refers to the cancers that begin in the muscle wall or tissue of the uterus (womb) when uterus cells grow out of control. The uterus or womb is a part of the female reproductive system. It is a muscular hollow organ in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. During the pregnancy, a fetus grows and develops in the uterus.
Metastatic uterine cancer involves the spreading of cancer cells to other organs.
It is very important for you to learn how bad (severe) your symptoms are.
How bad is my uterine cancer?
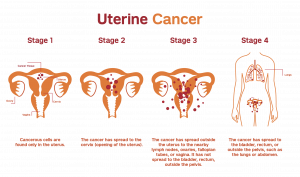
Stage I: Cancer has no spread except uterus. The stage is categorized into subgroups (IA, IB) to describe cancer in detail. The standard treatment for this stage is a total hysterectomy, which involves removing the uterus and cervix. The ovaries and fallopian tubes may also be removed, depending on the age and hormone status of the patient. Radiation therapy may be recommended after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
II: the cancer has spread to the cervix, but it remains within the pelvis. The standard treatment is a radical hysterectomy, which involves removing the uterus, cervix, upper vagina, and nearby lymph nodes. Radiation therapy may also be recommended after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
III: Cancer spread to the pelvic area without any distant metastases. The stage is sub-divided into subgroups (IIIA, IIIB, IIIC1, IIIC2). The treatment may involve surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible, followed by chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Hormonal therapy may also be considered.
IV: Cancer spread to the rectum, bladder, and distant body parts. The stage is sub-divided into smaller groups (IVA, IVB). The treatment may involve chemotherapy and radiation therapy to shrink the cancer and relieve symptoms. Hormonal therapy may also be used to control the growth of the cancer.
Warning signs/severe symptoms of Uterine cancer that need immediate medical attention
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain
- Abnormal vaginal discharge.
- Difficulty urinating or defecating
- Abdominal swelling
- Weight loss
What tests are needed to diagnose a uterine cancer?
CA-125 assay measures CA-125 protein. A certain level of CA-125 indicates cancer in the body.
Transvaginal ultrasound: The doctor inserts a smooth rounded device into the vagina to get images of the uterus.
MRI: The radio waves and strong magnets help make precise images of the affected area. MRI identifies the size of cancer and other tumors in the uterus.
Biopsy: The doctor removes the pieces of the uterus lining with a long, hollow needle to check it for cancer cells.
CT scan: It uses x-rays to create detailed images of the body. A CT scan detects the spread of cancer outside the uterus.
Hysteroscopy: The doctor inserts a tiny telescope or a long thin tube through the vagina and cervix to reach the uterus. It has a light and camera to capture detailed images of the uterus.
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a complex procedure to remove affected uterine tissue.
PET scan: It detects the cancer spread. The doctor puts a small amount of a low-level radioactive substance into the blood. The substance attaches to the cancer cells. A special camera shows any areas of radioactivity.
What caused my Uterine cancer
- Hormonal imbalances
- Obesity
- Age
- Family history
- Reproductive history
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Tamoxifen
What to expect after treatment?
You are always worried about cancer coming back or a recurrence. Keep all follow-up visits. Your doctors will ask you about the symptoms. A physical examination and diagnostic tests may help to check recurrence.
For the first year, the follow-up visits may be every three months. After the first year, follow-up visits might be every six months, and then at once a year after five years.
How can Ankr help with your Uterine cancer?
Don’t try to treat uterine cancer by yourself. Use Ankr to:
(1) learn about the common symptoms of uterine cancer
(2) send message to your Doctor if they use Ankr platform*
(3) be better informed about how to prevent another uterine cancer
