Table of Contents
What is peripheral neuropathy?
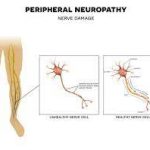
Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder of the peripheral nerves (nerves that lie outside brain and spinal cord). Peripheral neuropathy describes many conditions caused by damage to the peripheral nervous system. It can affect a single nerve or range of nerves and a variety of locations in different ways.
There are three types of nerves depending on their specific functions:
- sensory nerves carry signals about touch, taste, sight, hearing, pain and smell.
- motor nerves are responsible for muscle control and body movement.
- autonomic nerves are responsible for regulating autonomic body functions such as balance, sweating, digestion and bladder function.
Peripheral neuropathy usually affects the sensory nerves (hands, feet, arms or legs). But sometimes the autonomic nerves and motor nerves can also be damaged.
How bad is my peripheral neuropathy?
Mild: Usually it is asymptomatic. Sometimes you may experience tingling and numbness in the feet or hands. Most of the time, it can be safely managed at home.
Moderate: The symptoms are burning sensation in the feet or hands, muscle weakness, loss of sensation in the feet. It may limit instrumental activities of daily life (preparing meals, managing money, shopping, doing housework, and using a telephone).
Severe: It’s important to see a doctor if you have aching, cramps, loss of balance, weakness, a cut or ulcer on the foot that is not getting better. It may limit self-care activities of daily life (eating, dressing, getting into or out of a bed or chair, taking a bath or shower, and using the toilet).
How to manage mild peripheral neuropathy?
Keep track of your symptoms using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the discomfort to your doctor or nurse.
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean protein to keep nerves healthy.
- Protect against vitamin B-12 deficiency by eating meats, fish, eggs, low-fat dairy foods and fortified cereals. If you’re vegetarian or vegan, fortified cereals are a good source of vitamin B-12, Talk to your doctor about B-12 supplements.
- Exercise regularly. Try to get 30 minutes to one hour of exercise thrice a week.
- Avoid factors that may cause nerve damage (repetitive motions, cramped positions that put pressure on nerves, exposure to toxic chemicals, smoking and overindulging in alcohol).
- Manage medical conditions (diabetes, alcoholism or rheumatoid arthritis) that put you at risk.
How to manage moderate and severe peripheral neuropathy?
Seek medical care right away if you notice unusual tingling, weakness, or pain in your hands or feet. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help you control the symptoms and prevent further damage.
What causes peripheral neuropathy?
- Certain cancer treatments (Chemotherapy)
- HIV drugs
- B12 or folate vitamin deficiencies
- Chronic kidney disease: An imbalance of salts and chemicals can cause peripheral neuropathy.
- Injuries: Broken bones and tight plaster casts can put pressure directly on the nerves.
- Infections: Shingles, HIV infection, Lyme disease, and viral illnesses.
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (a specific type of peripheral neuropathy triggered by infection).
- Autoimmune disorders (rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Certain types of of cancer (lymphoma and multiple myeloma)
- Chronic liver disease
