Table of Contents
What are hives?
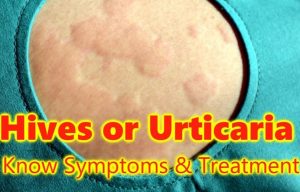
Hives or urticaria is a skin condition in form of raised, red bumps on your skin that can be itchy. It appears on the surface of your skin. You can get them at any age. You may get them once in your lifetime or repeatedly. Certain types of cancer can cause chronic hives (red, itchy skin that last more than six weeks).
How bad are my hives?
Severity of hives is based on how much of your skin is affected by it. It is called body surface area or BSA.
Mild: Lesions covering less than 10% BSA. For example, your arm or the top of your chest are about 9% BSA. Mild urticaria is generally treated with creams and lotions prescribed by your doctor. Some tips on managing mild symptoms are given below as well.
Moderate: Lesions covering 10 -30% BSA; oral treatment is necessary
Severe: Lesions covering 30% BSA; medical treatment is necessary
How to manage mild hives?
Keep track of your lesions using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the discomfort to your doctor or nurse.
- If you know the various causes, try to avoid triggers.
- Avoid tight clothes for long periods
- Take enough rest
- Wash your hands regularly
- Avoid extreme temperature changes
- Apply an anti-itch cream
- Cover the area with a cold cloth
- Take a hot bath or shower in cases of cold-induced hives
- Avoid alcohol, tobacco, and exercise
How to manage moderate and severe hives?
A severe case may cause swelling in the throat, face, tongue, or wheezing. This makes it difficult to breathe or swallow. Seek medical help if it covers a large part of the skin. You may need a shot of epinephrine or steroids.
What are the causes?
- Pollen
- Animal dander
- Insect bites
- Medicines
- Food, such as shellfish, fish, nuts, eggs, and milk
- Certain materials, such as wool or latex
- Allergic reactions
Other causes include:
- Stress
- Hay fever
- Infection or illness
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Tight clothing
- Quick change in body temperature
- Extreme weather change
