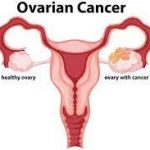
Ovarian cancer falls under the ‘Gynaecological cancer’ category. Women have two ovaries. These are female reproductive organs that produce eggs and women’s hormones. Ovarian cancer is the overgrowth of ovary cells. Ovarian cancers can start in the fallopian tubes, which connect the ovaries to the uterus.
What are signs & symptoms?
The common symptoms of ovarian cancer are flatulence (bloating), feeling of fullness, abdominal pain (bellyache), and frequent urge to pee.
What are the diagnostic tests for ovarian cancer?
- Ovarian biopsy: The doctor removes the pieces of the cancerous part of the ovary with a long, hollow needle. It is the only way to assure if you have cancer.
- CT scan: It creates detailed images of the body using x-rays. A CT scan detects the spread of cancer outside the ovaries.
- Ultrasound: The test involves inserting a tiny probe into the vagina or abdominal skin to produce sound waves. The sound waves create a picture of the ovaries on a computer screen.
- Laparoscopy: It uses a thin, lighted tube to check the ovaries and other body parts. It helps to detect the tumor spread and plan treatments, including surgery.
- Blood tests: It helps to identify the high levels of some proteins.
How advanced is my ovarian cancer?
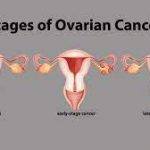
Ovarian cancer is classified as stages I, II, III, IV.
Stage I
It is the early stage of ovarian cancer. The cancer is only in your ovaries.
Stage II
Cancer spread to nearby organs, excluding lymph nodes and distant organs.
Stage III
Spread to nearby organs, including the uterus, stomach, lymph nodes, and bladder.
Stage IV
The most advanced stage where cancer spread to distant organs.
You can discuss with your doctor about the stages.
What are the suitable treatments for me?
Several kinds of treatment are available for ovarian cancer, including surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy.
SURGERY
Surgery helps to cure or control cancer and make symptoms better. It helps to cure ovarian cancer if not spread to other body parts. The standard ovarian cancer surgeries are total hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo, omentectomy, lymphadenectomy, colectomy, and unilateral salpingo.
The common side effects of cancer surgery are pain, nausea, fatigue (tiredness), and changed bowel habits.
Ask the doctor about the kind of surgery needed and what to expect.
RADIATION Therapy
Radiation destroys cancer cells left in the ovaries after surgery. There are two ways to treat ovarian cancer with radiation. The first is by aiming the rays at the ovaries from a machine outside the body. The second is by putting radioactive pellets, or tiny seeds, into the vagina near the ovaries.
The common side effects are fatigue, diarrhea (dysentery), frequent urge to urinate, and burning sensation.
Most side effects may improve after radiation ends. Ask your doctor about what to expect.
CHEMOTHERAPY
You can take chemo medicines intravenously or orally. The drugs spread through the body via the blood. Chemo is divided into cycles or rounds. After every cycle of treatment, there is rest time. Chemo is helpful if cancer has spread outside the ovaries.
Intraperitoneal chemotherapy injects chemo drugs directly into the abdominal cavity (the space between the abdominal organs and the abdominal wall). Intraperitoneal chemotherapy is beneficial for women with stage III disease. It is preferred over intravenous chemotherapy.
The common side effects are fatigue, body pain, infection, numbness, and hair fall. These side effects go away after chemo treatment ends. If you have side effects, discuss them with your doctor.
TARGETED THERAPY
Targeted therapy drugs are helpful for certain types of ovarian cancer. These drugs majorly affect cancer cells and rarely normal cells. The drugs move inside the cancer cells and block particular proteins or enzymes that nourish cancer cells.
Delayed wound healing, bleeding, high blood pressure, and kidney ailments are the common side effects. Ask your doctor if any complications arise.
What are the other treatment options?
The other treatment options may or may not be standard medical treatments. These treatments include vitamins, herbs, and diets. Talk to your doctor about other treatment options.
What to expect after treatment?
You may have fear of cancer recurrence. Visit your doctor every three months after the treatment ends. Do not skip follow-up visits. Your doctors will ask you about new symptoms. A physical examination and diagnostic tests may help to check recurrence.
For the first year, the follow-up visits may be every three months. After the first year, follow-up visits might be every six months, and then at once a year after five years.
Dealing with cancer is challenging. Ankr can help you find the best treatment and cut side effects by half! Sign up for free 30-day trial now (https://my.ankr.us/patientSignup) Ankr is the useful Cancer Platform in and around the USA. It offers the best modern treatment for cancer. Hence, improving the quality and life expectancy of the cancer patients.
