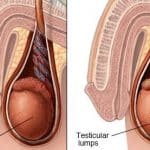
Testicular cancer is common cancer seen in men aged between 20 to 39 years. Testicular cancer occurs when healthy cells in a testicle form a malignant tumor that can spread to other body parts. The testicles are part of the male reproductive system. Typically, there are two testicles located in the scrotum(a sac-like pouch) in the male genital system.
Types of testicular cancer
- Seminoma is the most common cell type of testicular cancer in men aged between 25 and 45. It grows slowly and reacts well to surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Therefore, active surveillance (monitoring) is often helpful for early-stage seminomas.
- Non-seminomas are more common in younger men in their late teens or early 20s. It multiplies quickly and is less responsive to radiation and chemotherapy. Initial treatment involves surveillance and surgery. Chemotherapy is useful for later stages.
What are the symptoms?
- Heaviness in the scrotum
- Pain in the lower abdomen, the testicle, or scrotum
- Back pain
- Lump or swelling on either testicle.
- Shortness of breath (Dyspnea)
- Chest Pain
What are the diagnostic tests for testicular cancer?
- Testicular ultrasound helps check a suspicious lump in the scrotum.
- A blood test helps to check tumor markers. These are proteins and hormones made by some testicular cancers. Ask your doctor about your tumor maker levels.
- CT scan helps doctors find any abnormalities or tumors. For example, if a tumor is visible in the CT pictures, the scan can help measure the tumor size.
- MRI scan creates a 3-dimensional picture of the internal body. An MRI can be useful to measure the tumor size, location and spread to regional structures.
- PET scan produces pictures of organs and tissues inside the body. With the help of a radioactive sugar substance. The cancer cells absorb radioactive substance. A scanner detects the radioactive substance and produces images showing where the presence of cancer in the body. PET scans can be helpful in cases of pure metastatic seminoma.
- Biopsy removes a small amount of tissue for microscopic examination(histopathological examination) to identify the nature of the disease.
How advanced is my testicular cancer?
Stage 1: The cancer is present only in the testicle.
2: Cancer spreads to the lymph nodes in the abdomen or pelvis.
3: Cancer spreads beyond the lymph nodes to other body parts such as the lungs and liver.
What are the suitable treatments?
Surgery
- Orchiectomy is helpful to diagnose and treat early-stage as well as later-stage testicular cancer. It removes the entire testicle and through a incision given in the groin. After surgery, regular surveillance helps to ensure cancer free survival.
- Testis-sparing surgery (TSS) is beneficial in several cases. It removes the tumor tissue. It is best for men with benign tumors. Regular surveillance is necessary because cancer can recur.
- Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) is an option for patients with stage I cancer with a high risk for regional spread. It is also beneficial for non-seminomatous tumors.
Radiation
It kills cancer cells on the testis or in nearby lymph nodes. Radiation is helpful to treat seminoma-cell cancers. It may be an option if testicular cancer (either type) has spread to distant organs like the brain(known as distinct metastasis).
Chemotherapy
It is helpful for cancers that spread beyond the testicles(advanced cases) or if tumor markers is elevated after surgery. The chemotherapeutic drugs travel through the body in the bloodstream to eliminate cancer cells and lower the risk of cancer recurrence. Sometimes, combination chemotherapy treatment is beneficial for testicular cancer treatment.
What are the other treatment options?
The other treatment options may or may not be standard medical treatments. These treatments include vitamins, herbs, and diets. Talk to your doctor about other treatment options.
What to expect after treatment?
You may have fear of cancer recurrence. Visit your doctor every three months after the treatment ends. Do not skip follow-up visits. Your doctors will ask you about new symptoms. A physical examination and diagnostic tests may help to check recurrence.
For the first year, the follow-up visits may be every three months. After the first year, follow-up visits might be every six months, and then at once a year after five years.
Dealing with cancer is challenging. Ankr can help you find the best treatment and cut side effects by half! Sign up for free 30-day trial now (https://my.ankr.us/patientSignup) Ankr is the useful Cancer Platform in and around the USA. It offers the best modern treatment for cancer. Hence, improving the quality and life expectancy of the cancer patients.
