Table of Contents
What is malignant pleural effusion?
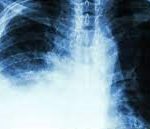
A malignant pleural effusion (MPE) is the build-up of fluid and cancer cells that collects between the chest wall and the lung.
Pleura is a thin layer of tissue that surrounds your lungs and lines the inside of your chest cavity. A small amount of fluid in this area is normal. It helps the lungs move in your chest as you breathe. Cancer and other conditions can cause fluid to build up. A pleural effusion can be serious and life-threatening, if left untreated.
How bad is my malignant pleural effusion?
Keep track of your symptoms using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the discomfort to your doctor or nurse.
Mild: You might not have any symptoms but most of the people experience dry cough.
Moderate: The symptoms are fever, cough, inflammation and hiccups. Your doctor may suggest some dietary changes (fat-restricted diet).
Severe: See your doctor immediately if you have chest pain, difficulty in breathing when lying down and pain in your chest, which may get worse when taking a deep breath.
How to manage mild symptoms?
Treatment for a pleural effusion can be given in a hospital or an outpatient setting. There are several methods (thoracentesis, tube thoracostomy, Catheter, shunt, surgery) available to remove the fluid.
How to manage severe malignant pleural effusion? ?
It can cause uncomfortable side effects. Seek medical help if you experience
- Shortness of breath
- Pain
- Feeling of chest heaviness or tightness
- Inability to lie flat
- Inability to exercise
What are the causes?
- Certain types of cancer:
- Breast Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Lymphoma
- Mesothelioma
- Ovarian Cancer
2. Cancer treatments: Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, abdominal surgery, and certain medications can cause pleural effusion.
3. Other health conditions:
- Blood clot in the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Heart disease or heart failure
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Pneumonia
- Airway obstruction or lung collapse
- Poor nutrition, causing low protein levels
