Table of Contents
What is choking?
Food or small objects can cause choking by blocking the airway. It restricts oxygen supply to the lungs and brain. If the brain goes without oxygen for more than four minutes, it may cause brain damage or death. It is a medical emergency that requires fast and appropriate action.
Certain cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation or surgery may causes dysphagia (Painful swallowing) and choking.
How bad is my choking?
Mild: You may experience coughing, gagging or wheezing while eating.
Moderate: Your skin may appear blue around the face, lips and fingernail beds. You may experience sudden inability to talk.
Severe: You won’t be able to speak, cry, cough or breathe. You may feel like something is stuck in the throat. It requires immediate treatment under your doctor’s supervision.
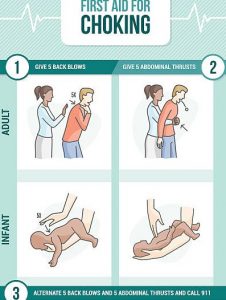
How to manage choking?
Keep track of your symptom using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the discomfort to your doctor or nurse.
- It is best not to do anything if the person is coughing forcefully and not turning a bluish color. Ask, “Are you choking?” If the person is able to answer you by speaking, it is a partial airway obstruction. Stay with the person and encourage him or her to cough and clear the obstruction.
- Do not give the person anything to drink because fluids may take up space needed for the passage of air.
When to visit a doctor?
Someone who cannot answer by speaking and can only nod the head has a complete airway obstruction and needs emergency help.
What causes choking?
- Esophageal cancer
- In older adults, risk factors are advancing age, poorly fitting dental work, and alcohol consumption.
- In adults, unchewed food, talking or laughing while eating may cause a piece of food to “go down the wrong pipe.
- Chewing food incompletely, attempting to eat large pieces of food or too much food at one time, or eating hard candy may causes choking in children.
