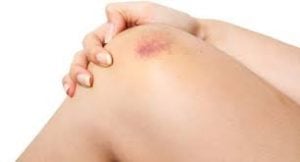
Bruising is a mark on the skin caused by blood trapped under the surface. It happens when an injury ruptures small blood vessels. Those vessels break open and leak blood under the skin.
Patients undergoing cancer treatment may often experience bruising which gets reduced once the treatment is stopped.
Bruises are often painful and swollen. You can get skin, bone, and muscle bruises. Bone bruises are the most serious. It can take months for a bruise to fade. Most of them last about two weeks.
Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and targeted therapy, can increase the risk of bruising.
How bad is my bruising?
Mild: It involves localized bruising (bleeding from smaller blood vessels) which typically doesn’t require medical treatment as such. The bleeding occurs at dependent area associated with the blood vessel. You can safely manage such conditions by taking the measures mentioned below.
Moderate: It involves generalized bruising (bleeding from larger blood vessels), discoloration of the skin, pain and swelling. It can be managed by the supportive care treatments mentioned below in general.
Keep track of your symptoms using Ankr (myAnkr web portal or the Ankr app). It will help you describe the uneasiness to your doctor or nurse.
Severe: No bruising is categorized as severe. You need not visit Doctor as the removal of the cause will mitigate the symptoms.
How to manage symptoms after bruising?
- Use an ice pack to reduce swelling. Wrap the pack in cloth to avoid putting it directly on your bruised skin. Leave the ice on your bruise for 15 minutes. Repeat this every hour as needed.
- Rest the bruised area.
- If possible, raise the bruised area above your heart to keep blood from settling into the bruised tissue.
- Take an over-the-counter medication, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), to reduce pain in the area. Avoid aspirin or ibuprofen as they may increase bleeding.
- Wear tops with long sleeves and pants to protect bruise on your arms and legs.
Warning signs/severe symptoms of bruising that need immediate medical attention
- Unexplained bruising, especially in a recurring pattern
- Bruise that aren’t painful
- Bruise that reappear in the same area without injury
- Any black bruises on your legs
What caused my bruising?
- Bruises can occur in some people who exercise vigorously, such as athletes and weight lifters. These bruises result from microscopic tears in blood vessels under the skin.
- Cancer treatments lower the number of blood platelets that help the blood to clot and stop bleeding.
- A bleeding disorder, especially if the bruising is accompanied by frequent nosebleeds or bleeding gums.
- Bumps into a bedpost or other object and fails to recall the injury.
- Bruises in elderly people frequently occur because their skin has become thinner with age.
- Bruises are also more common in those taking medicine to thin the blood.
How can Ankr help with your bruising?
Don’t try to treat a bruise by yourself. Use Ankr to:
(1) learn about the common symptoms of bruising
(2) send message to your Doctor if they use Ankr platform*
(3) be better informed about how to prevent another bruising
