Table of Contents
What is BCG?
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) is an anticancer biologic response modifier. This drug contains live, but weakened bacteria that cause inflammation of your bladder wall which in turn stimulates your immune system to kill cancer cells in the bladder. The drug itself stays in your bladder for two hours and is then drained out through the urinary catheter, or leaves your bladder when you pass urine. Your medical team may refer to BCG by its trade names: TheraCys® or TICE® BCG.
What is BCG Used for?
- Bladder cancer
Your Doctor may recommend this same drug for other problems if they believe it might be helpful.
How BCG Is Given:
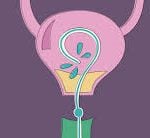
- It is given by intravesicular infusion. This means it is given directly into the bladder through a urinary catheter. The urinary catheter is inserted through the urethra (the tube which carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body). The BCG solution is injected into the catheter, which is then clamped. Clamping the catheter allows the medication to remain in the bladder. The patient is encouraged to roll from side to side and to lie on their backs to help the medication reach all areas of the bladder. After a predetermined time (usually about 2 hours) the catheter is unclamped and the fluid is drained. The catheter is then removed.
- BCG treatment is given as an outpatient procedure.
- The treatments are usually given on a weekly basis for 6 weeks followed by treatments once a month for 6 to 12 months. Your doctor will determine your exact treatment schedule and dose.
The amount of BCG that you will receive depends on many factors, including the manufacturer of the product you receive (there are multiple), your general health or other health problems, and the type of cancer or condition you have. Your doctor will determine your exact dosage and schedule.
What are the Side Effects of BCG?
Important things to remember about the side effects of BCG:
- Most people do not experience all of the side effects listed.
- BCG side effects are often predictable in terms of their onset, duration and severity.
- The side effects will improve after therapy is complete.
- The side effects may be quite manageable. There are many options to minimize or prevent the side effects of BCG.
The following side effects are common (occurring in greater than 30%) for patients taking BCG:
- Fatigue
- Bladder Problems (Painful or difficult urination, urgency, urinary frequency)
- Urinary frequency
- Blood in the urine (hematuria) (see bladder problems)
- Flu-like symptoms: fever, chills, malaise, fatigue, generalized aches and pains.
These are less common side effects (occurring in 10-29%) for patients receiving BCG:
- Bladder infection
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Genital pain
- Nephrotoxicity (kidney problems)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Anorexia (loss of appetite)
A rare, but potentially serious side effect is called systemic BCG reaction. This systemic reaction can occur following exposure to BCG within one week of either biopsy, TUR (trans-urethral resection) surgery, or traumatic bladder catheterization. Symptoms of a systemic BCG reaction include unexplained high fever lasting 24-48 hours or more, chills, confusion, dizziness or lightheadedness (symptoms of low blood pressure) or shortness of breath. It can cause pneumonitis (inflammation in the lungs), hepatitis (inflammation in the liver), prostatitis (inflammation in the prostate gland), epididmal-orchitis (inflammation in the testes), respiratory distress and other symptoms of sepsis (systemic infection).
Not all side effects are listed above. Side effects that are very rare — occurring in less than about 10 percent of patients — are not listed here. But you should always inform your health care provider if you experience any unusual symptoms.
When To Contact Your Doctor or Health Care Provider:
Contact your healthcare provider immediately, day or night, if you should experience any of the following symptoms:
- breathing problem
- Confusion
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
The following symptoms require medical attention, but are not an emergency. Contact your health care provider within 24 hours of noticing any of the following:
- Fever of 39.5 degrees C (103 degrees F) or higher within 24 hours.
- Fever of 38.5 degrees C (101 degrees F) or higher after 48 hours.
- Blood in the urine.
- Extreme fatigue (unable to perform self-care activities).
- Fever, chills, malaise, flu-like symptoms, increased fatigue or an increase in urinary symptoms (such as burning or pain on urination) are not uncommon. However, if these increase in severity, or last more than 48 hours let your doctor know.
Always inform your health care provider if you experience any unusual symptoms.
What Precautions are Needed?
- Before starting BCG treatments, make sure you tell your doctor about any other medications you are taking (including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or herbal remedies).
- BCG may be inadvisable in tuberculin positive individuals.
- Inform your health care professional if you are pregnant or may be pregnant prior to starting this treatment. Pregnancy category C (use in pregnancy only if benefit to mother outweighs risk to the fetus).
- To avoid transmission of BCG to others, for 6 hours after treatment patients should void (urinate) while seated to avoid splashing of urine. Urine voided during this time should be disinfected with 2 cups of household bleach into the toilet water and letting it stand for 15-2 minutes before flushing.
- Men having this treatment can pass on BCG during sex. To protect your partner from coming into contact with BCG, you should not have sex for 48 hours after each treatment. Use a condom if you have sex at other times during the treatment course and for six weeks after treatment has ended.
- For both men and women: Do not conceive a child (get pregnant) while taking BCG treatments. Barrier methods of contraception, such as condoms, are recommended while taking BCG. Discuss with your doctor when you may safely become pregnant after therapy.
- Do not breast-feed while taking this medication.
Self-Care Tips:
- Limit fluid intake for 6-10 hrs before treatment and for 2 hours following installation of BCG, afterward resume normal fluid intake.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol on treatment days. This is due to the diuretic (causing increased urine) and irritant properties of these substances.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Maintain good nutrition.
- If you experience symptoms or side effects, be sure to discuss them with your health care team. They can prescribe medications and/or offer other suggestions that are effective in managing such problems.
Monitoring and Testing:
You will be monitored regularly by your doctor while you are receiving treatment with BCG. Your doctor will order blood tests and other tests as needed to monitor side effects and check your response to therapy.
Trade names: TheraCys®, TICE® BCG
Last Updated: 02/27/21 A
