Table of Contents
Overview
External beam radiation therapy (also called EBRT, or sometimes just “RT”) is a radiation oncology procedure. It uses high-dose radiation to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. A machine aims radiation at cancer with high accuracy when treating a specific body part.
EBRT is used to treat several cancers, including breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, uterine, leukemia, melanoma, and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Types of external beam radiation therapy
3-D conformal radiation therapy
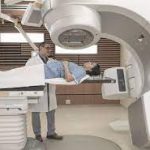
Here, CT, MRI, and PET scan images help plan the treatment area. A computer program analyses the images to design radiation beams that conform to the tumor shape.
How it works
It delivers beams from different directions. The precise shaping helps to use higher radiation doses on cancer.
Treatment schedule
The treatment is given once a day on weekdays. The number of treatments varies according to the type, stage, and size of cancer.
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)
It is an advanced type of 3-D conformal radiation therapy to treat cancer and noncancerous tumors.
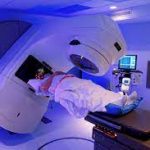
How it works
The small radiation beams are targeted at the tumor from different directions. It is possible to change the beam strength in some areas to give higher doses.
Treatment schedule
Generally given once a day on weekdays. The number of treatments varies according to the type, stage, and size of cancer.
Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT)
It uses imaging scans for treatment planning and during radiation therapy sessions.
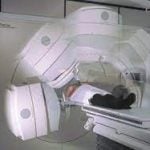
How it works
The computer processes CT, MRI, or PET, scans to detect tumor size and location. The repeated imaging helps the radiation dose to be adjusted during the treatment. It improves the accuracy of treatment.
Treatment schedule
The treatment is given once a day on weekdays. The number of treatments depends on the type, stage, and size of cancer.
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)
It uses high-energy and high-focused beams to treat brain and central nervous system tumors. It is an option if surgery is risky due to age, health problems, or tumor location.
How it works
A head frame limits the movement during treatment. The small radiation beams are targeted at the tumor from various directions. Each beam has a precisely aimed radiation dose delivered to the site.
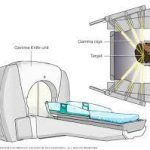
Treatment schedule
The treatment is given once a day in a single dose or up to five doses.
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)
It is useful for small, isolated tumors located outside the brain and spinal cord. It is useful when surgery is not an option due to age, health problems, or the tumor location.
How it works
It uses special equipment to hold the body during treatment. It delivers a precise beam to the limited area.
Treatment schedule
Stereotactic radiation is given once a day in more than one dose, up to five doses.
Side effects
Standard radiation therapy treatments may cause side effects depending on the treatment period and the body part being treated. For example:
- Skin changes
- Fatigue (Tiredness)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair Loss
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty swallowing
- Tenderness and inflammation
- Urinary symptoms like burning, blood in urine, pain
Questions to ask before treatment
- What will be the length of the therapy?
- What happens before the first treatment?
- How to relax before treatment sessions?
- What to wear for treatment?
- What happens during a treatment session?
- Will external beam radiation therapy make me radioactive?
What is proton therapy?
EBRT can be given using two types of particles:
- photons
- protons
Photons (LIGHT PARTICLES)
The machine uses photon beams to reach the tumor. These beams can give off (“scatter”) some of their energy along their path and it also doesn’t fully stop after reaching the cancer. This is why photon beams cause some of their side effects in normal tissue in their path (like diarrhea because of gut inflammation).
Protons
Proton particles can reach tumors deep in the body without scattering radiation along their path. They stop once they get to the cancer, thus decreasing healthy tissue’s exposure to the radiation. It doesn’t always work better than regular photon-based EBRT, but proton-beam therapy is generally used for brain cancer and cancers in children.
